Teradata is one of the most popular RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) in the field of data warehouses. Teradata is suitable for large data warehouse applications.
Teradata can handle large volumes of data quite easily. Teradata archives this by using the concept called pluralism. Teradata is developed by a company called Teradata.
Our Teradata tutorial is designed for both beginners and professionals.
What is Teradata?
Teradata, developed by Teradata Corporation, is one of the most popular RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) in the field of data warehouses. This was mainly designed for developing large-scale data warehousing applications.

Teradata RDBMS can run on Unix, Linux, and Windows server platforms.
History of Teradata
Initially, Teradata was a part of NCR Corporation which was incorporated in 1979. It was parted away from NCR in 2007.
Following is the summary of the major milestones of Teradata.
- 1979 – Teradata was incorporated.
- 1984 – The first database computer, DBC/1012, was released.
- 1986 – Fortune magazine declared Teradata as ‘Product of the Year’.
- 1999 – the most extensive database built using Teradata with 130 Terabytes.
- 2002 – the Teradata version V2R5 was released with compression and Partition Primary.
- 2006 – the Teradata Master Data Management solution was launched.
- 2008 – Teradata 13.0 version was released with Active Data Warehousing.
- 2011 – Acquires Teradata Aster and plunges into the Advanced Analytics Space.
- 2012 – the Teradata 14.0 version was introduced in the corporation.
- 2014 – the Teradata 15.0 version was introduced in the corporation.
- 2015 – the Teradata Bought Apps Marketing Platform Appoxee.
- 2016 – Terada joined hands with Big data.
- 2017 – Teradata Acquired San Diego’s StackIQ.
Why use Teradata?
There are plenty of reasons to choose Teradata over other database systems for large applications.
- Linear scalability helps to support more users/data/queries/query complexity without losing performance. When system configuration grows performance increases linearly.
- The system is built on open architecture, so whenever any faster chip and device are made available it can be incorporated into the already build architecture.
- Automatic distribution of data across multiple processors (AMP) evenly. Components divide tasks into approximately equal pieces so all parts of the system are kept busy to accomplish the task faster.
- Supports 50+ petabytes of data.
- Provides a parallel-aware Optimizer that makes query tuning unnecessary and gets it run efficiently.
- Single operation view for a large Teradata multi-node system via SWS (Service Workstation). This is mainly managed by Teradata GSC.
- Single point of control for the DBA to manage the database using Teradata viewpoint.
- Compatible with large numbers of BI tools to fetch data.
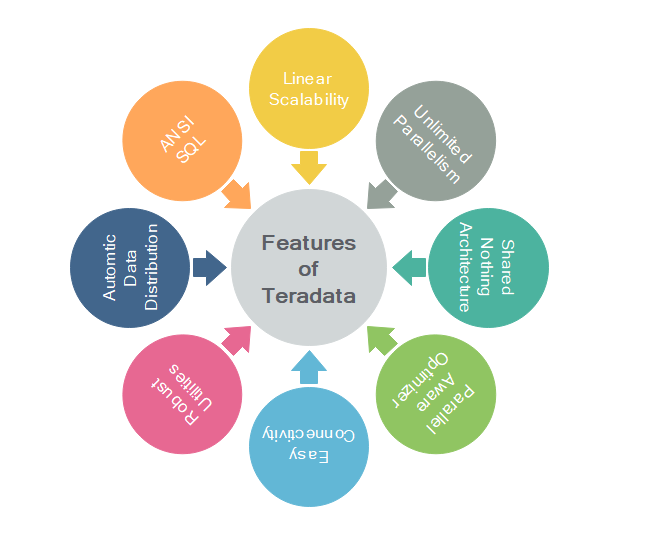
Features of Teradata
1) Linear Scalability
Scalability defines to increase the processing power by increasing the hardware configuration. Teradata is a highly scalable system. They can be expanded up to 2048 nodes and creates a highly powerful database system. For example, 4 nodes system is double-powerful than two nodes system with the same node configuration.
2) Unlimited Parallelism
The architecture of Teradata is built on massively parallel processing (MPP) which helps to execute any task in a faster manner. MPP architecture divides the task evenly across the entire system. Teradata system splits the task among its virtual processes (AMP) and runs them in parallel to ensure that the task is completed quickly.
3) Shared Nothing Architecture
Teradata system is a shared-nothing architecture in which each node is independent and self-sufficient. Also, each logical processor (AMP) is responsible only for its own portion of data.
4) Parallel aware optimizer
Teradata provides one of the most advanced optimizers in the market which is built to be parallel since its inception. The optimizer is also refined in each release.
5) Easy Connectivity
Teradata systems can be connected using Channel-attached systems such as Mainframe or Network-attached systems.
6) Robust Utilities
Teradata provides robust utilities to import/export data from/to Teradata systems such as FastLoad, MultiLoad, FastExport, and TPT.
7) Automatic Data Distribution
Teradata automatically distributes the data evenly to the disks without any manual intervention.
8) SQL
Teradata supports industry standard ANSI SQL to communicate with the database.